Exploring the Brain's Connection to Music


Intro
In our world, music isn’t just a background noise or entertainment. It’s a profound element that interlinks with the very essence of how our brain functions. The human experience is rich with auditory emotions, shaped largely by melodies and rhythms that resonate in our minds. But how exactly does music mold our brain's workings? This article peels back the layers to reveal the intricate web woven between sound and neural processes.
Understanding this relationship sheds light on how music influences our thoughts, feelings, and actions. For instance, when a catchy tune gets stuck in your head, it isn’t mere chance; it’s a glimpse into the brain's fascinating mechanics. Music is not only an art form but a tool that can strengthen cognitive abilities and evoke emotional responses.
Technology Insights
Latest Tech Trends
As we march into a more technology-driven era, the ways we engage with music are evolving. Digital platforms like Spotify and Apple Music have transformed the music landscape. With algorithms finely tuned to our preferences, these platforms learn our listening habits and curate personalized playlists. This technology doesn’t just offer convenience; it alters how we perceive music.
Recent innovations in music-making software, such as Ableton Live and Logic Pro, empower creators with previously unattainable tools. The lines between the artist and the techie are increasingly blurred.
Innovation in Tech
Wearable technology is also enhancing our musical experiences. Devices like the Muse Headband allow users to meditate with guided music, tuning their brains to specific frequencies for relaxation. This has opened avenues for therapeutic uses of music, suggesting a synergy between tech and mental well-being.
With the rise of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), concerts are no longer confined to physical spaces. VR enables anyone to experience live performances from the comfort of their home, which presents unique opportunities for cognitive engagement through immersive environments.
Product Reviews
When considering music production, Native Instruments Komplete stands out as an essential tool for composers and sound designers alike. The extensive library provides a treasure trove of sounds and effects that encourage creativity. For those who wish to dive into sound therapy, the Brainwave Entrainment app can be invaluable, allowing individuals to leverage music as a healing medium.
"Music can change the world because it can change people." - Bono
Emotional Impact of Music
Music does not only cater to our auditory senses; it affects our emotions on a grand scale. From classical symphonies to modern pop hits, the melodies can evoke a spectrum of feelings. Studies indicate that listening to music triggers the release of dopamine, the brain's feel-good neurotransmitter, fostering joy and pleasure.
Cognitive Benefits
Moreover, engaging with music can enhance memory and concentration. This effect has been utilized in educational settings, where teachers incorporate songs and rhythms to aid students in memorizing complex information. It’s a tactic that reflects the brain's ability to form strong associations between melodies and data.
Therapeutic Applications
In many therapeutic settings, music therapy has emerged as a remarkable practice for mental health. It can aid in addressing disorders such as anxiety or depression. The rhythmic patterns and harmonies offer a medium for expression that transcends words, fundamentally unlocking emotions that might otherwise remain suppressed.
Closure
The interplay between music and the human brain is a captivating subject, one that extends far beyond mere enjoyment. Each beat, each melody holds potential to dapple our cognitive functions and emotional landscapes. As technology continues to bridge these domains, our understanding of music's profound role in human life will only deepen.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a music lover, or simply an individual curious about cognitive science, exploring the convergence of these elements reveals a compelling facet of our reality. Embracing this knowledge not only shapes our musical journey but enhances our overall well-being.
Preamble to the Brain-Music Connection
Understanding how music and the brain interact is not just a niche study; it has implications for our daily lives, our health, and even our social interactions. The interplay between these two forces—music and brain function—shapes our experiences in profound ways. Music not only serves as a form of entertainment but also acts as a powerful tool for cognitive stimulation, emotional release, and social connection. The way our brains respond to music provides insights into human behavior and culture itself.
Understanding the Basics of Brain Function
At its core, the brain is a complex organ responsible for countless functions that make us who we are. An intricate network of neurons communicates through electrical impulses and chemical signals. When we listen to music, our brain's auditory cortex becomes active, processing sound waves. However, the magic doesn’t stop there. Various regions of the brain spring into action: the temporal lobes handle rhythm and melody, while the limbic system is key in processing emotions.
The brain is remarkably adaptable. Neuroplasticity, or the brain's ability to reorganize itself, means that experiences—including musical training—can physically touch our brain structures for the better. Regular interaction with music can enhance synaptic connections, improving both cognitive and emotional responses.
Brief History of Music in Human Culture


Music has been an integral part of human life since time immemorial. From primitive drum beats that echoed in tribal ceremonies to the symphonies of Beethoven, music has woven itself into the fabric of societies worldwide. Early humans used music as a means of communication, celebration, and mourning. It was a way to bond within groups, ensuring that experiences were shared and feelings expressed.
The advent of technology has revolutionized music-making and consumption. With the invention of the phonograph in the late 19th century, music became accessible to the masses. This trend has only accelerated with the digital age, where streaming platforms allow instant access to a rich tapestry of sounds from around the globe.
The impact of music on culture is undeniable; it transcends linguistic barriers, evokes memories, and fosters a sense of belonging. As we delve deeper into the relationship between music and the brain, we uncover how this relationship has evolved with us, molding not just music itself but our very existence.
Neurological Responses to Music
Understanding how music affects our brains opens up an intriguing window into human cognition and perception. Music is more than just a sequence of notes; it’s a catalyst for a complex array of brain activities that engage various areas responsible for emotional, cognitive, and sensory processing. This section examines the critical neurological responses to music, shedding light on why music is not only an art form but also a powerful tool for enhancing both mental and emotional health.
The Processing of Sound in the Brain
When we listen to music, sound waves travel through air before reaching our eardrums, but the journey doesn't stop there. These vibrations are transformed into electrical signals and sent to different parts of the brain. This process occurs primarily in the auditory cortex, which is located in the temporal lobe. Here, the brain decodes aspects like pitch, rhythm, and volume.
Interestingly, our brains tend to process music much like a language. This suggests that the connection between music and language might be more intertwined than previously thought. In fact, research has indicated that music and speech share similar neural pathways. This unique way of processing sound allows for a emotional depth in music that often resonates deeper than mere words can convey.
Moreover, neural imaging studies have shown that engaging with music activates regions of the brain associated with reward, such as the nucleus accumbens. This area is particularly responsive to pleasurable stimuli, which explains why a catchy tune can stick to your mind like glue.
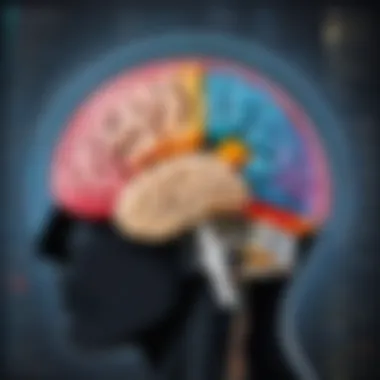
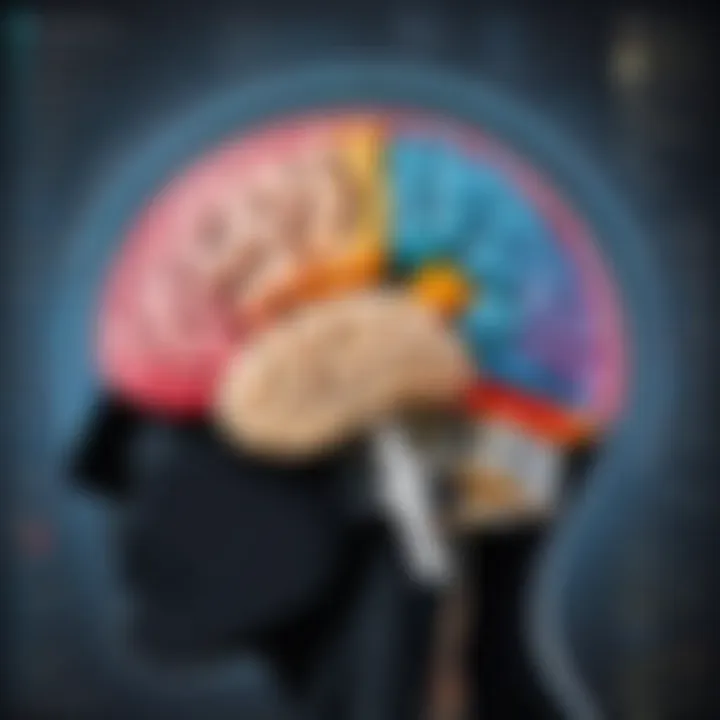
Brain Regions Involved in Musical Perception
Many areas of the brain come into play when we experience music. The primary regions include:
- Auditory Cortex: As mentioned, this area processes the sounds we hear, analyzing everything from melody to rhythm.
- Prefrontal Cortex: This part is associated with decision-making and social behavior. It plays a role in our ability to understand and predict musical structures, contributing to our enjoyment of music.
- Limbic System: Often considered the emotional brain, it comprises structures like the amygdala and hippocampus, which are crucial for emotional responses and memory recollection. The limbic system’s involvement explains why a familiar song can evoke powerful memories or feelings.
- Motor Cortex: Interestingly, this region shows activity when we engage in music, even if we are just tapping our feet or nodding our heads. Studying how music triggers physical responses provides insight into its rhythmical nature and our instinctual reactions.
Neurotransmitters and Music Appreciation
Neurotransmitters, or chemical messengers in the brain, play a vital role in how we experience music. Dopamine, in particular, is crucial. When you listen to your favorite song, your brain releases dopamine, which creates feelings of pleasure and reward. This chemical response is often similar to what happens when we consume food or experience other rewarding stimuli.
Other neurotransmitters like serotonin and oxytocin may also come into play, influencing mood and social bonding. This biological basis for music appreciation could explain why music can be such a universal bridge between people, cross cultures and generations. Listening to music is not just a passive activity; it triggers a dynamic interplay of chemicals that enhance feelings of connection and happiness, enriching our lives in profound ways.
"Music is a world within itself; it’s a language we all understand." - Stevie Wonder
In summary, the neurological responses to music are multifaceted, encompassing auditory processing, emotional engagement, and intricate brain activity. By understanding these connections, we can begin to appreciate not just music as an art form, but as an essential aspect of what makes us human.
The Emotional Impact of Music
The emotional resonance of music is a powerful aspect that makes it not only an art form but also a profound psychological tool. Understanding how music impacts our emotions offers great insights into human experience and can reveal why melodies stir memories or why certain tunes make us feel alive. The interplay between music and emotion is significant as it taps into our personal histories—our joys, sorrows, triumphs, and losses. Every individual brings their own lens to musical interpretation, making the emotional experience of music as varied as the listeners themselves.
How Music Evokes Emotion
Music can provoke a spectrum of feelings, ranging from sheer joy to deep melancholy. The mechanisms behind this evoke a complex blend of auditory processing and psychological reaction. One way this happens is through the structure of music—rhythm, melody, and harmony each play critical roles in setting the emotional tone. For instance, a lively tempo can inspire feelings of happiness and energy, while slower, minor-key melodies might resonate with feelings of introspection or sadness.
Consider the role of lyrics too. Songs that tell personal or relatable stories can strike a chord with listeners, triggering emotional responses based on their experiences. For example, a ballad reflecting loss might bring comfort to someone grieving, while an anthem of triumph can energize and inspire.
Ultimately, music acts as a sonic mirror. The emotions we experience while listening often reflect our own internal states, colored by past experiences and mood. It’s this reflective quality of music that makes it a unique and personal experience, allowing us to engage deeply with the emotional currents it offers.
Music and Memory: A Deep Connection
The connection between music and memory is another intriguing aspect of how music impacts our emotions. This relationship can be traced back to the brain's architecture. Research suggests that the areas of the brain responsible for processing music are closely linked to the areas that manage memory. When we listen to a familiar tune, it can transport us back to a specific moment in time, often loaded with emotional significance.
Using music as a mnemonic device is a common practice, particularly in educational settings. For instance, children often learn through songs, making curricular information stick more effectively in their minds. This is not limited to just learners; adults report that nostalgia induced by music can enhance the clarity of their memories. A particular song playing while sharing a significant moment can imbed that memory deeply.
Cognitive neuroscience has also documented the impact of music in therapeutic contexts, particularly for those with memory impairments. For instance, patients with Alzheimer’s disease may recall memories linked to songs from their youth, bridging connections that other stimuli may not trigger. Music's ability to evoke strong memories is a testament to the emotional depth woven into the fabric of sound.
Case Studies on Music-Induced Emotions
To illustrate the emotional impact of music, several case studies have surfaced in recent years, showcasing how music influences emotional states across diverse populations. In one study, conducted by researchers at the University of Groningen, participants were exposed to various musical pieces while monitoring their physiological responses. The findings indicated significant changes in heart rate and sweat production that correlated with emotional fluctuations elicited by the music played.
In another instance, the use of music in therapeutic settings showed remarkable effects. A study with cancer patients revealed that listening to calming music significantly reduced their anxiety levels before surgery, proving once again that the right tune at the right time can enact a powerful change in emotional well-being.
These real-world implications underline how integral music is to the emotional fabric of human life, bridging gaps of understanding and connection among individuals across different backgrounds. Mapping such emotional journeys not only enriches our understanding of music but also serves as a profound testament to its indispensable role in human experiences.
Cognitive Effects of Music on the Brain
The relationship between music and cognitive functions has been the subject of many studies, revealing an intricate web of interactions that play a significant role in human development and mental health. Understanding these cognitive effects could lead to transformational approaches in education and therapy. The benefits can be as varied as improving memory recall to enhancing problem-solving abilities. This section sheds light on how music touches various facets of cognition, making it an essential area of exploration in our journey to comprehend the brain-music connection.
Music's Influence on Cognitive Development
From an early age, the exposure to music can profoundly shape cognitive abilities in children. Research indicates that kids who engage with music tend to perform better in areas like language development, spatial reasoning, and even mathematical skills. A simple rhyme or catchy tune can lead to improved retention of information. This ability can sometimes be traced back to actively listening to songs or playing musical instruments, both of which stimulate various brain areas.
"Exposure to music during formative years can set the stage for lifelong learning capabilities."
Involvement in music also fosters patience, perseverance, and discipline, which ultimately contributes to cognitive growth. Thus, integrating music into educational settings could be a game-changer in developing learning strategies that harness these cognitive benefits.
Enhancing Learning through Music
Integrating music into learning environments can create a more engaging and effective atmosphere. It’s been noted that background music can aid concentration and reduce distractions. The right types of music, especially classical or instrumental, provide a calming backdrop that can enhance one's focus.
For instance, students who listen to certain genres while studying show improved outcomes in assessments and information retention. Moreover, songs that incorporate educational content can make learning feel less like a chore. This leads us to reflect on how sound plays an active role in memory encoding and recall.
Incorporating music in classrooms can take various forms:
- Interactive Music Games: These can enhance participation and retention.
- Chanting or Singing Exercises: These contribute to rhythmic memorization of facts.
- Playlists with Specific Themes: Certain playlists can energize students or help them relax based on the study requirements.
The Role of Music in Mental Health
Music has long been recognized as a therapeutic tool, helping individuals manage psychological conditions. The soothing qualities of certain melodies can alleviate anxiety, depression, and stress. Neurologically, engaging with music triggers the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that contributes to feelings of pleasure and reward.
In particular, music therapy has emerged as a crucial element in mental health care, mutually benefiting both clinicians and patients. Listening to preferred music or even creating it can contribute to emotional healing and stability. Various clinical settings have implemented music therapy with success, including:
- Hospitals: Using music to ease pain and discomfort.
- Rehabilitation Centers: Assisting with cognitive recovery through rhythm-based activities.
- Counseling Sessions: Facilitating verbal expression through descriptive lyrics and melodies.
Music, Society, and Evolution
The connection between music, society, and evolution plays a pivotal role in understanding the broader implications of musicality in human interaction and development. Music is more than just an art form; it shapes social structures, influences cultural identities, and has been integral in the evolution of human societies. The significance of this interplay lies in its ability to foster community, convey emotions, and enhance cooperation among individuals.
Music as a Social Bonding Tool
From time immemorial, music has served as a potent vessel for social bonding. Whether it’s singing around a campfire, dancing at weddings, or playing in orchestras, music creates shared experiences, dissolving barriers between people. In many cultures, communal musical activities are vital for fostering connections among community members.
- Shared Identity: Music helps forge a collective identity. National anthems and cultural songs instill a sense of belonging and shared history.
- Emotional Connectivity: When people engage in musical activities together, they often find themselves emotionally aligned, promoting empathy and understanding.
- Activism and Change: Music has a history of galvanizing social movements. Songs like "We Shall Overcome" evoke shared ideas and aspirations, often being the heartbeat of protests.
As such, music cultivates not just personal relationships, but communal bonds, creating a fabric of connection that supports societal wellbeing.
Evolutionary Perspectives on Music’s Role
Evolutionarily speaking, the roots of musical inclination may go far beyond simple enjoyment; they possibly served critical adaptive functions for early humans. Understanding this aspect reveals how music has embedded itself in our evolutionary narrative.
- Survival Mechanism: Some theorists posit that music accompanied social behaviors crucial for survival. Communicating emotions through song could have helped coordinate group activities, such as hunting or gathering, thereby boosting efficiency and safety.
- Mate Selection: On another note, music may enhance mate selection. Individuals who demonstrate musical talent might signal genetic fitness, which was beneficial in early human societies for attracting partners.
- Cognitive Evolution: The development of music likely spurred cognitive growth, pushing humans to engage in complex forms of communication and creativity.
This evolutionary approach adds another layer to our understanding of music—not simply as a cultural artifact, but as a fundamental aspect of human development that shaped social interactions across millennia. In summary, through social bonding and evolutionary adaptation, music stands as a testament to the adaptability and resilience of human societies.


Exploring Contemporary Research
The investigation of music’s impact on the brain has come into sharper focus in recent years. This pursuit is not just vital for academics but also for everyday individuals who seek to understand the intricate web that binds auditory experiences with cognitive processes. By exploring contemporary research in music and neuroscience, we can uncover various facets that influence emotional health, learning, and overall brain functioning.
Advances in Music Neuroscience
Recent studies have shed light on the nuances between music and its profound effects on brain function. Neuroscientists are now employing advanced imaging techniques, like fMRI and PET scans, to paint a more detailed picture of how the brain reacts to different genres of music. One notable case involved researchers studying how classical compositions stimulate brain areas responsible for complex decision-making and emotional regulation.
These findings hold several benefits:
- Understanding Neural Mechanisms: Researchers are identifying specific brain networks activated by music, leading to insights into how music can be integrated into therapeutic practices.
- Music's Impact on Brain Plasticity: If you think music is just for enjoyment, think again. Some studies suggest that regular engagement with music can reshape neural pathways, enhancing cognitive flexibility. This reshaping can be particularly beneficial for children, enhancing their learning capabilities continuously into adulthood.
- Applications in Neurorehabilitation: Innovative music-based interventions are now being designed for stroke recovery, demonstrating that listening to or creating music can speed up brain recovery. This has proven promising, especially with patients experiencing motor function deficits.
Technological Innovations in Music Therapy
The intersection of technology and music therapy is paving new paths for healing and well-being. From apps designed to personalize music experiences to devices that utilize biofeedback for therapeutic purposes, contemporary research suggests exhilarating possibilities.
Some exciting innovations include:
- Music-Assisted Therapy Apps: Developments like Melodic Connections and Brain.fm offer structured activities combining music and cognitive training to encourage mental agility in patients suffering from conditions like PTSD or anxiety disorders.
- VR in Music Therapy: Virtual Reality experiences incorporating music allow users to engage with therapeutic environments. One research team recently explored how VR coupled with soothing music can help in managing pain during medical procedures, highlighting its effectiveness in reducing distress.
- Wearable Technology: Smart gadgets that monitor emotional states and adjust music accordingly are gaining traction. For instance, devices may shift music tempo or style based on a user’s heart rate or skin response, offering tailored therapeutic experiences.
"Innovations in music therapy exemplify the blend of science and art, showcasing how technology can optimize health outcomes and enhance well-being."
In summary, contemporary research into music's interplay with brain function presents a treasure trove of opportunities for both individuals and society. With each advancement comes a deeper understanding of how music can improve emotional and cognitive health, ultimately forming bridges between creativity and neuroscience.
The Future of Music and Brain Research
The exploration of the interplay between music and the brain is ushering in a new era of understanding and innovation. As we stand on the cusp of groundbreaking discoveries, the importance of focusing on the future of music and brain research cannot be overstated. This research not only reveals the underlying mechanisms through which music affects our cognitive and emotional states but also shapes how we can leverage these insights for practical applications in various fields.
Notably, the advent of advanced neuroimaging techniques has revolutionized our ability to visualize the brain in action. This means researchers can observe real-time responses to music, opening avenues to understand how different genres and rhythms impact brain activity. Insights gleaned from these studies can provide valuable information about personalization of therapy and education, allowing individuals to engage with music in a way that optimally caters to their neural structure.
Furthermore, as the demographics of society continue to change, so does the relationship we have with music. Understanding these shifts will guide musicians, educators, and healthcare professionals alike in crafting experiences that resonate on a deeper level.
Emerging Trends in Music Psychology
The field of music psychology is witnessing several emerging trends, driven largely by technology and a growing cultural appreciation for the arts. One notable trend is the application of artificial intelligence in music generation and personalization. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data from listener behaviors and preferences, helping create music tailored to individual tastes. This not only enhances consumer experiences but also poses questions about originality and creativity in music.
Moreover, research is increasingly focusing on how music interacts with mental health. We’re beginning to see how certain types of music can act as therapeutic tools for conditions ranging from anxiety to PTSD. Music therapists are increasingly adopting a more data-driven approach, utilizing metrics obtained from brain scans to determine which musical elements can yield the best outcomes for specific populations.
Potential Implications for Education and Therapy
The intersection of music, education, and therapy holds tremendous promise. As we harness our understanding of music's cognitive and emotional effects, there arise opportunities for innovative educational methodologies. For instance, music-infused learning environments can foster better engagement and retention of information. Subjects can be taught in stimulating ways that incorporate musical elements, enhancing the learning curve notably.
In therapy, music's therapeutic implications span a broad spectrum. By using rhythm and melody as tools for emotional expression, therapists can facilitate healing in ways traditional talk therapy may not fully achieve. Group music activities can strengthen social bonds and foster a sense of community among participants. This approach highlights the need for mental health professionals to continue evolving their practice to incorporate music-based interventions.
"Music is not only a means of expression but also a bridge to unlocking the inner workings of the mind."
The collective understanding of these potential implications arms us with the knowledge to utilize music effectively, thereby improving quality of life for individuals across various settings. The future of music and brain research looks bright, and as we keep digging into these developmental threads, we can expect remarkable advancements that will enrich human experience.
Ending: The Enduring Power of Music
When we delve into the depths of human experience, music emerges as a profound constant. It resonates across cultures and generations, binding us together in ways that surpass simple auditory pleasure. The significance of the relationship between the brain and music is layered and rich, impacting emotions, cognition, and even our physiological states. As emphasized throughout this article, music doesn't merely exist in isolation; it shapes and reflects our very being.
Reflecting on the Brain-Music Interconnection
Key Considerations of the Interconnection:
- Emotional Impact: The brain processes music through the limbic system, which is closely linked to emotions. Thus, a single note can evoke nostalgia or joy, enhancing our emotional landscape.
- Cognitive Functioning: Research indicates that music training can improve memory and focus. This speaks volumes about harnessing music for educational advancements.
- Therapeutic Potentials: Music therapy is becoming a recognized means of aiding mental health, offering therapeutic pathways for everything from anxiety to trauma recovery.
- Social Connections: Music nurtures bonds, whether through communal listening or performing together, underlining its role as a social glue in various contexts.
“Music is the shorthand of emotion” – Leo Tolstoy
This quote encapsulates the essence of why understanding the brain-music relationship matters. By appreciating how music involves the brain, we unearth practical applications that can transform lives. This understanding not only enhances the educational philosophies but also approaches to therapy, inviting us to consider ways to integrate music into daily life for sustained emotional and cognitive health.
As we conclude this exploration, it is evident that music's power is not only enduring; it is essential. Our evolving understanding of how music impacts brain function could very well lead to revolutionary approaches in education and therapy and foster deeper connections among individuals. Hence, as we move forward, let us remain open to music’s profound potential in shaping our realities and enriching our existence.







