Exploring the Left and Right Brain: Cognitive Insights
Intro
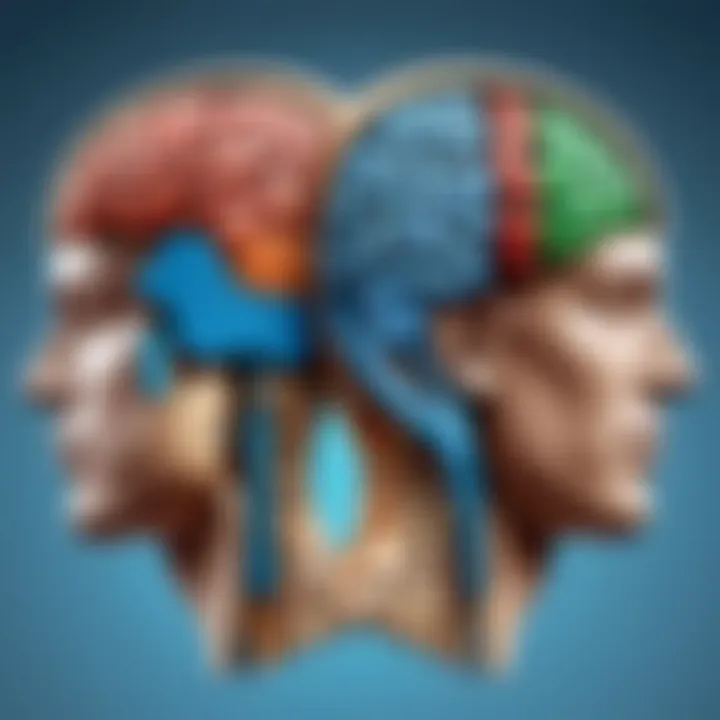
The intricacies of the human brain have long fascinated both researchers and the general public. Understanding the functionality of the left and right hemispheres can provide important insights into our cognitive abilities and how we process information. The conventional understanding of brain lateralization attributes specific tasks to each hemisphere. The left hemisphere is often connected with logic, analytical thinking, and language. In stark contrast, the right hemisphere is associated more with creativity, intuition, and emotional responses. Knowing these distinctions not only helps in academic and professional fields but also plays a significant role in everyday life.
This discussion stems from ongoing debates in neuroscience and psychology about the extent and meaning of these hemispheric differences. As we delve deeper into the subject, we aim to unpack these historical contexts and contemporary research findings, elucidating mental processes and their impact on mental health and education. It is crucial to discern what myths might surround the perception of left-brain versus right-brain thinking, ensuring a greater understanding of individual differences in cognitive functionalities.
By entertaining an educated perspective on how brain walls blur in real-life scenarios, individuals can utilize their cognitive strengths more effectively, leading to greater advancements in personal development.
Technology Insights
The intersection of neuroscience and technology provides fertile ground for understanding how we can enhance cognitive functions. Significant strides in brain-computer interfacing showcase how we can tap into the benefits of understanding our brain's structure. Recent innovations provide methods that speed up the cognition process, bridging communication gaps for those with disabilities. Tools and software rooted in neuroscience research allow users to monitor their cognitive health and mental performance.
Latest Tech Trends
That there is a growing trend in cognitive enhancement technologies combining artificial intelligence with neurological studies is no surprise, particularly in fields like education and productivity. Here are a few notable trends:
- Biofeedback devices that help users modify their mental states based on real-time data.
- Cognitive training apps which are designed to enhance memory and attention skills.
- Virtual reality experiences tailored to modify emotional responses through simulated environments.
Innovation in Tech
Innovation in technologies related to understanding brain functionalities shows promise for future advancements. Companies are developing devices that measure brain activity, such as neurostimulation headsets and wearable sensors. Some studies suggest that regular usage can improve focus and cognitive alertness.
While the effectiveness of such technologies is still under research, early adopters are keen to explore their potential benefits, especially in dynamic sectors needing continual mental effort.
Product Reviews
As consumers look for methods to optimize their brain power, products like the Muse meditation headband gain popularity. Muse provides real-time feedback on meditation practices through audio cues derived from brain activity.
Another notable device is the Focus@Will service, which offers music designed to enhance concentration. Users report markedly improved productivity when engaged with intended soundscapes crafted with specific brain states in mind.
Ultimately, advancing our understanding of the left and right brain can quite literally enhance how one interacts with the worlds of technology and thought, leading specializations that thrive on the collaboration between biological insight and digital intelligence.
Understanding what drives the mind could very well complement these agile innovations shaping our day-to-day functions.
Prelims to Brain Lateralization
Brain lateralization refers to the division of cognitive functions between the two hemispheres of the brain. Understanding this concept is vital for grasping how our brain processes information and drives behavior. This article explores various aspects of lateralization, scrutinizing how the left and right hemispheres offer distinctive functionalities. These differences can impact everything from everyday activities and interpersonal communications to more specialized talents such as creativity or analytical reasoning.
Lateralization also emphasizes the interdependence of these two hemispheres. Each side complements the other, facilitating more complex thought systems. Therefore, acknowledging this collective functioning can lead to a deeper comprehension of cognitive capabilities. Ultimately, brain lateralization shapes not only personal development but can also provide insights into educational practices and mental health approaches. By dissecting the core principles of lateralization, we gain valuable perspectives on individual differences in thinking styles and abilities.
Definition and Overview
Brain lateralization is fundamentally about the specialization of the brain's hemispheres. The left hemisphere typically handles tasks related to language, logic, and analytical processes. In contrast, the right hemisphere is skilled in visual activities, spatial abilities, and emotional interpretation.
The brain communicates through a band of nerve fibers known as the corpus callosum. This structure allows the two hemispheres to share information, enforcing an integrated system capable of multifaceted approaches to problem-solving.
The understanding of the brain’s lateralization has profound implications in various fields, including education and psychology.
Historical Background
The concept of brain lateralization is not new. Research has roots in the early 19th century when scientists began observing the effects of brain injuries on mental functioning. One prominent figure, Paul Broca, discovered specific areas corresponding to language processing in the left hemisphere during his studies on patients with speech impairments. This marked a pivotal moment in neuroscience.
Soon after, other researchers, like Carl Wernicke, contributed additional insights, showcasing different cognitive functions attributed to either side. Neuroimaging techniques developed in the late 20th century advanced our understanding of brain connections further, allowing for precise mapping of functional areas. Today, contemporary methodologies continue to build upon these findings, illuminating deeper aspects of cognitive performance subjected to lateralization.
Potential benefits of fostering analytical thinking include:
- Greater clarity in understanding complex systems
- Enhanced performance on critical tests and assessments
- Improved decision-making processes
Mathematical Abilities
Mathematics is not merely a subject processed in the left hemisphere; it represents a fundamental characteristic of its functionality. This hemisphere supports numerical processing and spatial analysis, essential for solving equations. It fosters the development of logical reasoning necessary for understanding in fields like science and finance. Mathematically inclined individuals often excel in calculations and algebraic manipulations, revealing a connection to left-brain functions. For professionals engaged in technological roles, honing mathematical facilities can lead to efficient algorithms or innovation in data analytics.


The comprehension of mathematical concepts demonstrates not just practical abilities but also underpins technology's growth.
As the left hemisphere contributes significantly to language, analytic thinking, and mathematics, understanding its unique attributes is vital for both educational success and cognitive development. Recognizing these skills allows for tailored strategies that capitalize on left-hemisphere strengths, fostering holistic personal and professional growth.
The Right Hemisphere: Functions and Characteristics
The right hemisphere of the brain plays a crucial role in various cognitive functions and characteristics. Understanding its unique contributions helps to provide a more comprehensive view of human cognition. This section explores the right hemisphere and its significant impact on areas such as creativity, emotional processing, and spatial capability.
Creativity and Artistic Expression
The right hemisphere is often associated with creativity and artistic expression. This region allows individuals to engage in imaginative thinking and innovative problem-solving. Many artists and musicians rely heavily on the functions governed by this hemisphere to create expressive works.
Research indicates that the right hemisphere processes visual and spatial information, enabling creatives to generate complex imagery and sound structures.
- It supports holistic thinking, allowing one to perceive patterns and connections that left-brain thinkers might overlook.
- It's vital for the comprehension of metaphors and symbolic concepts.
- This hemisphere plays a part in producing music, allowing musicians to improvise and evoke emotional responses in their audience.
In summary, individuals using strategies that incorporate right-hemisphere strengths can enhance their creative works and day-to-day problem solving.
Emotional Awareness and Interpretation
The right hemisphere also holds authority over many emotional functions. Strong emotional awareness leads to better interpersonal connections. It helps individuals to perceive and interpret emotional cues from others.
Key aspects of how the right hemisphere affects emotional functioning include:
- Facial Recognition: This area excels in interpreting expressions, assisting in empathy and social cues discernment.
- Emotional Literacy: Individuals with strong right-hemisphere abilities may articulate their emotions better and engage with others on an emotional level.
- Mood Regulation: It contributes to the processing of emotions, which help manage moods and mental well-being.
Such characteristics are essential not only for personal relationships but also for professional environments where teamwork and management of social dynamics are significant.
Spatial Abilities and Visualization
Spatial skills are another vital manifestation of right-hemisphere functionality. People who utilize this side effectively can navigate environments and visualize complex concepts.
- Navigation: Those with right-brain dominance may excel in tasks that require spatial navigation. This can be useful in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and even everyday activities.
- Visualization: Effectiveness in creating mental images aids in product design, artistic pursuits, and understanding spatial relationships in data representation.
- 3D Manipulation: Performing actions that require visualizing three-dimensional models depends heavily on right-hemisphere capabilities.
Overall, comprehension of the basic structure and functions of the right hemisphere can yield practical benefits in academics, work-related tasks, and personal projects. It highlights the need to support skills tied to artistic expression, emotional awareness, and spatial abilities, to optimize one’s capabilities.
In an increasingly complex world, understanding the right hemisphere’s contributions provides invaluable insights for enhancing both personal and professional capabilities.
Interconnectedness of the Hemispheres
Understanding the intricacies of the brain's functional connectivity is essential in grasping cognitive operation. The interaction between the left and right hemispheres allows for a spectrum of tasks that involve both analytical and intuitive approaches. This interconnectedness enables a balanced cognitive experience that impacts various aspects of life.
Corpus Callosum Functions
The corpus callosum is a critical bundle of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain. It plays a vital role in transmitting information across both sides. Through this communication channel, the hemispheres share knowledge, allowing cognitive integration. This is especially important in complex tasks, where synthesizing logical and emotional insights is necessary.
One important functon is motor coordination. When we perform activities that require significant joint efforts of both hands, the corpus callosum ensures that instructions are rapidly relayed between the hemispheres. Similarly, tasks requiring both detailed attention and creative problem-solving benefit from interconnected input. Without the functions of the corpus callosum, complex cognitive processes would not produce the refined output necessary for adept functioning in daily situations.
- Enhanced sensory perception: The corpus callosum enables seamless exchange of sensory data from both sides of the body.
- Improved problem-solving capabilities: Together, both hemispheres contribute to better solutions by engagin diverse approaches.
Strokes or injuries affecting the corpus callosum can lead to deficits that become evident in specific cognitive abilities, demonstrating the significance of this structure.
Collaboration Between Hemispheres
Effective collaboration between hemispheres yielded remarkable productivity in everyday functions. While the left hemisphere is primarily responsible for language, analytical functions, and details, the right hemisphere contributes perspectives on visual imagery and emotional context. The result is a pragmatic synthesis that enhances both learning and creative expression.
For teaching methods, understanding collaboration is crucial. Teachers can design curricula that engage both dance and rhythm while promoting language skills, using movement to stimulate cognitive engagement. This holistic education could furnish learners with approaches that cater to the diverse territories of the brain. Merging these techniques fosters a learning environment where students utilize cognitive strengths to overcome challenges.
A collaborative approach contributes to innovative ways in which technology can enhance training. Digital tools are increasingly awash in the challenge of intuitively combining comprehension with creativity. As artificial intelligence and brain-computer interactions become more popular, understanding this connectedness is increasingly relevant.
By teaching children that different activities can engage various parts of their brains, we not only improve performance academically and artistically, but also nurture their emotional intelligence. Emphasizing mindfulness practices within education systems can further bridge these interconnected hemispheres, consolidating the emotional experiences with logical reasoning. > “It is in this collaboration that we give way to many possibilities of the human mind.”


Incorporating this understanding yields several benefits:
- A more responsive educational strategy
- Improvement in emotional literacy
- Increased adaptability to classroom dynamics
The interplay of the left and right hemispheres demonstrates the comprehensive nature of cognition and its paramount importance for personal and educational development.
Impact on Learning and Education
Understanding brain lateralization is essential in the context of education and learning. The differentiation of functions between the left and right hemispheres facilitates tailored teaching strategies that consider the cognitive strengths of individual learners. The left hemisphere’s strengths in analytical thinking and language result in specific preferences for certain types of learning, while the right hemisphere’s focus on creativity and emotional processing captures different aspects of intelligence often underrepresented in conventional education.
The significance of integrating these insights into learning environments cannot be stressed enough. When educators recognize the intertwined roles of both hemispheres, they can develop a more holistic approach to teaching that enables students to leverage their brain functionality effectively. Whether it involves adopting right-brain-friendly activities in classrooms or utilizing left-brain focused instructional methods, understanding the impact of brain lateralization defines the direction of pedagogical strategies.
Teaching Strategies for Both Hemispheres
To address diverse cognitive styles among students, it’s crucial to implement teaching strategies that engage both the left and right hemispheres. Such strategies lead to more effective learning outcomes:
- Balanced Instruction: Teachers should encourage the use of both structured lessons that appeal to analytical thinking and open-ended tasks that promote creativity.
- Varied Assessment Methods: Assessments can be designed that allow students to showcase their understanding through different mediums – writing essays for left-brain learners and creating art projects for right-brain learners.
- Interdisciplinary Projects: Creating projects that incorporate elements of science, language, and art can engage a full spectrum of cognitive abilities.
- Collaborative Learning: Group activities that necessitate both analytical skills and creative approaches allow students to enhance their cognitive versatility by learning from each other.
By prioritizing a variety of teaching modalities, we help ensure students are respected for their unique cognitive profiles. This dual approach can maximize engagement by holding the interest of all members of the classroom, which in turn contributes positively to both educational outcomes and student motivation.
Cognitive Development in Children
Children's cognitive development significantly hinges on the activation of both hemispheres. Early years are particularly crucial, as this is when the foundational perceptions of learning, interpretation of emotions, and creative expression emerge. Research indicates that stimulating both sides of the brain can yield heightened academic performance and greater emotional resilience in children.
Focus on:
- Creativity: Encourage play-based learning, which usually promotes curiosity and is aligned with right-brain functions. Activities might include art projects, music, and dance that cater to young learners’ natural tendencies to imagine.
- Critical Thinking: Balancing creative endeavors with tasks such as puzzles or language-based activities fosters left-brain development.
- Multimodal Learning: Actionable experiences that join visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learning styles export benefits to developing both hemispheres. Examples of this can be involved sticky experiments with fresh fruits to illustrate colors and mathematics in simple form.
Promoting a blend of experiences that develop crucial cognitive skills early in life allows for a platform on which further intellectual growth can be constructed. Parents and educators should acknowledge that addressing the dual aspects of brain functionality will result not just in academic achievements but also shape well-rounded learners prepared for future challenges.
Psychological Perspectives on Brain Function
Understanding the mind involves examining various psychological approaches that define how we interpret mental processes, particularly in terms of the brain's functions. Psychological perspectives on brain function shed light on how cognitive processes are informed by the distinct capabilities of the left and right hemispheres. Exploring this relationship helps to integrate aspects of cognition, emotions, and thoughts, unravelling the richness of human psychology. Each perspective fills in parts of a greater puzzle, revealing a clearer picture of how we interact with the world. Understanding these perspectives contributes significantly to practical applications in clinical settings and education.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Brain Lateralization
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, often referred to as CBT, is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on changing maladaptive thoughts and behaviours. This approach hinges on the understanding that one’s perception and emotional responses affect overall behaviour and choices. Thus, its importance cannot be overstated in the context of brain lateralization.
Research suggests that the left hemisphere predominantly processes negative emotions, while the right hemisphere taps into positive emotions and emotional comprehension. This division provides key insights for mental health practitioners utilizing CBT; it emphasizes the necessity to target affected brain areas during treatment.
CBT does not merely treat symptoms but seeks to reshape thought patterns, enhancing brain functionality. Those familiar with the concepts of dual processing in neuroscience can appreciate how CBT aligns with hemispheric processing. This form of therapy aids character development, resilience, and emotional management in individuals across all walks of life.
Key aspects of this connection include:
- Emotion Recognition: Due to the right hemisphere's role in emotional awareness, CBT can align its methods to better engage emotional processing.
- Targeted Interventions: Tailored cognitive strategies could be developed based on the individual’s primary hemisphere engagement, maximizing treatment effectiveness.
Neuroscience of Emotions
The neuroscience of emotions underscores how deeply interlinked our emotions are with cognitive processes located within brain structures. Emotional responses govern behaviour, resolving the everyday struggle between thought and feeling. In the context of brain lateralization, it’s vital to understand how emotions influence cognitive reactions; the two cannot be isolated from each other.
Different biases and interpretative frameworks emerge from hemispheric specializations. While the right hemisphere is known for emotional regulation and recognition, the left hemisphere often engages in logical assessment. Interplay between the two leads to complex human responses, illustrating how grounded thoughts may affect emotional reactions, and vice versa.
An essential insight here is:
Emotional disturbances can trigger cognitive issues, reinforcing the view that effective treatment hinges on aoscilation between or engagement of both hemispheres.
In practical settings, recognizing these emotional processes can lead to better strategies for personal development, decision-making, and overall mental health management. Emphasizing the interplay between cognition and emotion supports a more holistic approach to understanding human behavior.
The importance of psychological perspectives on brain function is clear. As we delve deeper, these insights have immense implications for therapeutic practices, educational reform, and enhancing personal well-being.
Common Misconceptions About Left and Right Brain Theory


The topic of brain lateralization has led to widespread beliefs about how the left and right hemispheres govern distinct functions. Understanding the misconceptions surrounding left-brain versus right-brain theories is crucial in promoting a more accurate picture of cognitive functions. These myths can influence educational practices, corporate training programs, and self-assessments in personal development. Addressing the misconceptions can help avoid misguiding stereotypes. It creates room for evidence-based perspectives on how individuals best engage with their competencies.
Debunking Left-Brain vs.
Right-Brain Myths
The notion that individuals predominantly use either their left or right brain originated from early neurological research. It suggested clear-cut divisions of cognitive functionality. Proponents claimed left-brained individuals were logical, analytical, and focused on details, while right-brained individuals were seen as artistic, intuitive, and big-picture thinkers. However, these simple ideological constructs have been largely debunked by modern neuroscience.
Research indicates that cognitive activities seldom lie solely within one hemisphere. Instead, they require a collaboration of both sides. For example, parsing language, often attributed to the left hemisphere, also involves areas on the right. Tasks such as solving problems blend elements of creativity with logic, illustrating a fuller picture of brain function involving the entire cerebral cortex rather than a strict dichotomy.
- Critical Thinking: If a subject appears either analytical or creative, both hemispheres are engaged.
- Learning Styles: Educational strategies based on left-right brain theories often overlook the interconnectedness essential for comprehensive understanding.
“Neuroscience shows that complex brain functions are rarely isolated to a single hemisphere.”
Current Scientific Consensus
Current scientific consensus regards the left and right brain as part of an integrated system rather than opposing forces. While certain functions may favor one hemisphere, both are simultaneously engaged when a person undertakes most cognitive tasks. Studies through neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), reinforce this concept. These techniques deliver visual representations of brain activity, confirming that even tasks traditionally tagged for one hemisphere recruit both areas.
The ongoing dialogue within the scientific community helps address engagement in varied fields:
- Cognitive Psychology: It supports integrated approaches to therapy and learning rather than compartmentalized ideas based on hemispheric dominance.
- Neuroeducation: Curriculum design inclusive of various cognitive styles can leverage insights learned from this criticism of simplifications.
Practical Applications of Understanding Brain Lateralization
Understanding brain lateralization has significant relevance both in daily life and specialized fields. Knowledge of how the left and right hemispheres function can help individuals improve their communication skills, analyze their personal development, and facilitate growth. These practical applications enrich our interactions, cognitive processes, and mental well-being while also deepening our understanding of individual differences.
Enhancing Communication Skills
The ability to communicate effectively is crucial in various aspects of life, including professional and personal contexts. By recognizing whether one leans towards left-brain or right-brain traits, individuals can adjust their communication styles.
- Verbal Communication: Left-brained individuals often excel in verbal expression and analytical discussion. They can prepare and deliver messages using structured language. This ability makes them efficient in environments that require clarity and logic.
- Non-Verbal Communication: Right-brained individuals tend to be more attuned to emotions and artistic expression. They might convey ideas through body language, art, or storytelling, offering different dimensions to communication.
- Active Listening: Both brain types can enhance their communication by practicing active listening. Top skills include clarifying steps, summarizing others’ ideas, and validating emotions—encouraging deeper dialogues.
Ultimately, the understanding of brain laterlization promotes adaptability in communication. It enables individuals to read social cues and choose appropriate responses.”
Personal Development and Growth
The insights from brain lateralization can be instrumental in personal growth strategies for specific skills and attributes. Awareness of one's cognitive strengths nurtures better learning methods and life choices.
- Goal Setting: Left-brained individuals may find success in setting clear, structured goals, leveraging their logical thinking. On the other hand, right-brained individuals may excel when they pursue broader, flexible aspirations that allow for creativity.
- Skill Acquisition: Identifying cognitive strengths can optimize learning approaches. Left-brained individuals might benefit from methodical instruction and analytic study methods, while right-brained learners may thrive in labs, workshops, and through experiential learning.
- Emotional Intelligence: Awareness of one’s bilateral cognitive functions enhances emotional understanding. This leads people to foster empathy and compassion, essential traits for both personal and professional relationships.
Understanding the brain's intricate functionality is key for our interaction, thought, and creativity.
By leveraging these insights, individuals can reshape their cognitive development paths, gaining fluidity across mental functions.
Culmination and Future Directions
Understanding brain lateralization is crucial in numerous fields. The interplay between the left and right hemispheres reveals much about not only our cognitive strengths but also our emotional responses. Recognizing the differentiated functions of these hemispheres empowers educators, clinicians, and individuals working on personal growth.
Developing teaching strategies that leverage the distinct skills of each hemisphere can enhance instructional methods. For instance, engaging with both intuitive artistic practices and structured analytical activities fosters a well-rounded educational approach. As important, mental health practitioners can tailor their therapies based on the brain regions most engaged by their clients’ behaviors and thought patterns.
Moreover, being aware of how the left hemisphere excels in language and logical reasoning while the right hemisphere leads in creative thought can benefit neurodiverse individuals and broaden our understanding of different cognitive profiles.
Understanding the link between emotional intelligence and cognitive functionality is more than a mere curiosity. It is a foundation for mental health strategies and educational techniques that promise to cultivate more effective interactions and achieve individual growth.
Future research should aim to unveil deeper insights about the synaptic connections that enable communication between these hemispheres. Insights gained might lead to advances in treatment approaches for conditions like dyslexia or attention disorders.
Experimenting with new neurological assessment methods or developing neurofeedback practices may further harness the potential of the brain's plasticity. Continuous exploration will deepen comprehension of how we can influence cognitive abilities through tailored interventions and educational programs.
Summary of Key Findings
- The left hemisphere specializes in language, mathematical processing, and logical analysis.
- The right hemisphere is key in emotional awareness, creativity, and spatial understanding.
- The corpus callosum connects both hemispheres, facilitating collaboration for smoother cognitive processing.
- Misconceptions surrounding the 'left-brain' and 'right-brain' dimensions have overshadowed a nuanced understanding of cognitive functionality.
- Practical applications span multiple domains, including education and personal growth, affirming the social relevance of cognitive research.
Implications for Future Research
Research agendas could investigate multiple facets of brain lateralization, including:
- Advanced Neuroimaging Techniques: Utilizing new imaging technology to better map the colors of brain function at any level of complexity.
- Educational Psychology: Examining bisecting strategies and outcomes for teaching diverse learners across both hemispheres.
- Neuroscience and Mental Health: Exploring targeted therapeutics influencing emotional regulation linked with specific hemispheric activity.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: Developing exercises that improve interaction between the two hemispheres to support recovery from injuries or surgical interventions.
The interests in these areas are bound not just to expand theoretical applications but could also lead to impactful innovations in mental wellness practices and personalized education goals.







